Drugs
What is a drug?
A drug is any substance that alters the body’s Central Nervous System. There are seven categories of drugs:
(1) Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants
CNS depressants slow down the operations of the brain and the body. Examples of CNS depressants include alcohol, barbiturates, anti-anxiety tranquilizers (e.g., Valium, Librium, Xanax, Prozac, and Thorazine), GHB (gamma hydroxybutyrate), Rohypnol, and many other anti-depressants (e.g., Zoloft, Paxil).
(2) CNS Stimulants
CNS stimulants accelerate the heart rate and elevate the blood pressure and “speed-up,” or over-stimulate, the body. Examples of CNS stimulants include cocaine, “crack” cocaine, amphetamines, and methamphetamine (“crank”).
(3) Hallucinogens
Hallucinogens cause the user to perceive things differently than they actually are. Examples include LSD, peyote, psilocybin and MDMA (Ecstasy).
(4) Dissociative Anesthetics
Dissociative anesthetics include drugs that inhibit pain by cutting off or dissociating the brain’s perception of the pain. PCP, its analogs, and dextromethoraphan are examples of dissociative anesthetics.
(5) Narcotic Analgesics
Narcotic analgesics relieve pain, induce euphoria, and create mood changes in the user. Examples of narcotic analgesics include opium, codeine, heroin, demerol, darvon, morphine, methadone, Vicodin, and oxycontin.
(6) Inhalants
Inhalants include a wide variety of breathable substances that produce mind-altering results and effects. Examples of inhalants include Toluene, plastic cement, paint, gasoline, paint thinners, hair sprays, and various anesthetic gases.
(7) Cannabis
Cannabis is the scientific name for marijuana. The active ingredient in cannabis is delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC. This category includes cannabinoids and synthetics like Dronabinol.
What do drugs do?
Illegal drug use provides a quick escape from reality, creating happiness, joy, and excitement. However, just as quick as that escape occurs, so does the fall. Making you drowsy and nauseous, causing your body to hurt and can even cause death.
Alcohol
Excessive drinking, under the age of 21, accounted for approximately 4,300 deaths each year between 2006-2010, and cost the U.S. $24.3 billion in 2010 according to the CDC. Although binge drinking has significantly declined among U.S. high school students, underage drinking is still a persistent problem. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health reports about 5.8 million Americans between the ages of 12 and 20 consume alcohol. Students who take their first drink of alcohol before the age of 15 were 6.5 times more likely to experience an alcohol use disorder as an adult.
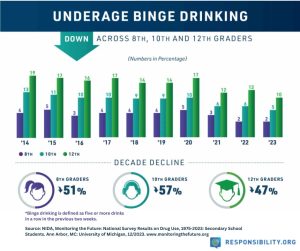
Underage Drinking Is Dangerous
Underage drinking poses a range of risks and negative consequences. It is very dangerous for the following reasons.
-
- Causes many deaths. Alcohol is a significant factor in the deaths of people younger than age 21 in the United States each year. This includes deaths from motor vehicle crashes, homicides, alcohol overdoses, falls, burns, drowning, and suicides.
-
- Causes many injuries. Drinking alcohol can cause youth to have accidents and get hurt. In 2011 alone, about 188,000 people younger than age 21 visited an emergency room for alcohol-related injuries.
-
- Impairs judgment. Drinking can lead to poor decisions about taking risks, including unsafe sexual behavior, drinking and driving, and aggressive or violent behavior.
- Increases the risk of physical and sexual assault. Underage binge drinking is associated with an increased likelihood of being the victim or perpetrator of interpersonal violence.
- Can lead to other problems. Drinking may cause youth to have trouble in school or with the law. Drinking alcohol is also associated with the use of other substances.
- Increases the risk of alcohol problems later in life. Research shows that people who start drinking before the age of 15 are at a higher risk for developing alcohol use disorder (AUD) later in life. For example, adults ages 26 and older who began drinking before age 15 are 3.5 times more likely to report having AUD in the past year than those who waited until age 21 or later to begin drinking.
- Interferes with brain development. Research shows that people’s brains keep developing well into their 20s. Alcohol can alter this development, potentially affecting both brain structure and function. This may cause cognitive or learning problems as well as may increase vulnerability for AUD, especially when people start drinking at a young age and drink heavily.
Why Do So Many Youth Drink?
As children mature, it is natural for them to assert their independence, seek new challenges, and engage in risky behavior. Underage drinking is one such behavior that attracts many adolescents. They may want to try alcohol but often do not fully recognize its effects on their health and behavior. Other reasons youth drink alcohol include:
- Peer pressure
- Increased independence or the desire for it
- Stress
In addition, many youth have easy access to alcohol. In 2022, among adolescents ages 12 to 14 who reported drinking alcohol in the past month, 97.7% reported getting it for free the last time they drank.14 In many cases, adolescents have access to alcohol through family members or find it at home.
Preventing Underage Drinking
- Individual-level interventions. This approach seeks to change the way youth think about alcohol so they are better able to resist pressures to drink.
- School-based interventions. These are programs that provide students with the knowledge, skills, motivation, and opportunities they need to remain alcohol-free.
- Family-based interventions. These are efforts to empower parents to set and enforce clear rules against drinking, as well as improve communication between children and parents about alcohol.
- Community-based interventions. Community-based interventions are often coordinated by local coalitions working to mitigate risk factors for alcohol misuse.
- Policy-level interventions. This approach makes alcohol harder to get—for example, by raising the price of alcohol and keeping the U.S. Minimum Legal Drinking Age at 21. Enacting zero-tolerance laws that outlaw driving after any amount of drinking for people younger than 21 can also help prevent problems.
Warning Signs of Underage Drinking
Parents, families, and teachers should pay close attention to the following warning signs that may indicate underage drinking:19,20
- Changes in mood, including anger and irritability
- Academic or behavioral problems in school
- Rebelliousness
- Changing groups of friends
- Low energy level
- Less interest in activities or care in appearance
- Finding alcohol among an adolescent’s belongings
- Smelling alcohol on an adolescent’s breath
- Problems concentrating or remembering
- Slurred speech
- Coordination problems
Tobacco & Vaping
What is Vaping? Isn’t it just “flavored water vapor?” No!
Vaping involves inhaling “e-juice” in the form of aerosol produced by an electronic cigarette or vape device. The aerosols typically contain flavorings such as diacetyl, a chemical linked to serious lung disease, nicotine and other harmful chemicals. Vape cartridges or “pods” can also be filled with THC, CBD or other “e-juice.”
Mass media show tobacco products being used by younger people, making students more likely to try those products. The use of tobacco in any form is unsafe for youth. It is Illegal for any person under 21 years of age to:
-
- Possess, Use, Consume Tobacco Products
- Purchase or attempt to purchase Tobacco Products
- Order, Pay for, or share cost of Tobacco Products
- Furnish a false identification card to obtain control over a Tobacco Product
Tobacco Product is any product made from or derived from Tobacco, or contains nicotine. Possession of tobacco products underage can result in an unclassified misdemeanor, probation, community service, suspension or fines.
- Includes: Cigarettes, Cigars, Pipes, Electronic Cigarettes (Juul, Vape), Chewing Tobacco, or snuff.
- Cigarette smoke is filled with more than 70 cancer-causing chemicals, including: Formaldehyde (also found in embalming fluid), Naphthalene (also found in mothballs), Toluene (also found in paint thinner), and lead.
E-cigarettes and vape devices come in a number of forms. While some resemble tobacco products, others resemble household objects like USB devices, pens, highlighters and chargers. Vaping devices like Puff Bar are designed for one-time use and are now disposable. E-cigarettes deliver a high level of nicotine very quickly, making them extremely addictive; each “pod” contains as much nicotine as a pack of cigarettes (nicotine is the third most addictive substance, following behind heroin and cocaine).







*Graphics from Wisconsin Department of Health Services and Lung.org
Nicotine is harmful to developing brains, affecting attention, learning, mood, impulse control, and memory. Nicotine use in youth can increase risk for addiction to other drugs as well; research shows that teens who have vaped are almost four times as likely to go on to smoke traditional cigarettes. The FDA is also investigating a link between seizures from nicotine overdose in kids caused by vaping.
What Smoking Does to Your Lungs
What are the signs of use that parents should look for? 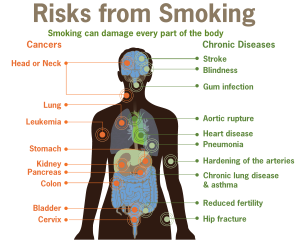
Vaping is easy to hide, and the signs can be easy to miss. Unlike traditional cigarettes, e-cigarettes don’t leave the telltale scent of tobacco. If you notice any of the following things, it’s best to talk with your child about whether or not they are vaping.
-
- Presence of unfamiliar technology, online purchases or packaging
- Faint sweet or fruity scents
- Behavioral and mood changes
- Increased irritability or restlessness
- Cutting back on caffeine
- Desire for flavor due to taste-bud degradation
- Pneumonia
- Increased thirst
- Nosebleeds
If you think you kid isn’t vaping, you might want to think again, over 10% of high-school students and 4.6% of middle schoolers currently vape as of 2022. The FDA and U.S. Surgeon General have declared it an epidemic.
